South Sudan - Government
Based on the etymolgy of South Sudan, it was self-descriptive name from the country's geographic position within Sudan prior to independence; the name Sudan derives from the Arabic balad-as-sudan, meaning "Land of the Black [peoples]". The Government system in this country is the presidential republic type and the different Administrative divisions includes: 10 states; Central Equatoria, Eastern Equatoria, Jonglei, Lakes, Northern Bahr el Ghazal, Unity, Upper Nile, Warrap, Western Bahr el Ghazal, Western Equatoria
National symbols
African fish eagle.
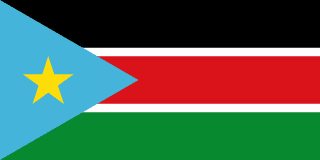
The flag
The National flag of South Sudan has .
Info
The National Anthem
| Title | |
|---|---|
| Lyric/music |
Info
More about the government of South Sudan
| Date of Independence | 9 July 2011 (from Sudan) |
|---|---|
| National holiday | Independence Day, 9 July (2011) |
| Legal system | |
| International law organization participation | |
| Constitution | |
| History | Previous 2005 (pre-independence); latest signed 7 July 2011, effective 9 July 2011 (Transitional Constitution of the Republic of South Sudan, 2011) |
| Amendment process | Proposed by the National Legislature or by the president of the republic; passage requires submission of the proposal to the Legislature at least one month prior to consideration, approval by at least two-thirds majority vote in both houses of the Legislature, and assent of the president |
| Citizenship | |
| Citizenship by birth | no |
| Citizenship by descent only | at least one parent must be a citizen of South Sudan |
| Dual citizenship recognized | yes |
| Residency requirement for naturalization | 10 years |
| Executive Branch | |
| Chief of state | President Salva KIIR Mayardit (since 9 July 2011) |
| Head of government | President Salva KIIR Mayardit (since 9 July 2011) |
| Cabinet | National Council of Ministers appointed by the president, approved by the Transitional National Legislative Assembly |
| Election/appointment process | president directly elected by simple-majority popular vote for a 4-year term (eligible for a second term) |
| Most recent election date | 11-15 April 2010 |
| Election results | 2010: Salva KIIR Mayardit elected leader of then-Southern Sudan; percent of vote - Salva KIIR Mayardit (SPLM) 93%, Lam AKOL (SPLM-DC) 7% |
| Expected date of next election | scheduled for 2015 but has been postponed multiple times, currently to be held in December 2026 |
| Legislative branch | |
| Legislature name | Législature nationale (National Legislature) |
| Legislative structure | Bicameral |
| Judicial branch | |
| Highest court(s) | Supreme Court of South Sudan (consists of a chief justice, deputy chief justice, and 5 additional justices); the 2011 Transitional Constitution of South Sudan calls for 9, rather than 5 additional justices |
| Judge selection and term of office | The 2011 Transitional Constitution of South Sudan calls for the establishment of a Judicial Service Council to recommend prospective justices to the president, and for the justices' tenures to be set by the National Legislature |
| Subordinate courts | National level - Courts of Appeal; High Courts; County Courts; state level - High Courts; County Courts; customary courts; other specialized courts and tribunals |
| Diplomatic representation in the US | |
| Chief of mission | Ambassador Santino Fardol Watod DICKEN (since 18 September 2024) |
| Chancery | 1015 31st Street NW, Suite 300, Washington, DC 20007 |
| Telephone | [1] (202) 600-2238 |
| FAX | [1] (202) 644-9910 |
| Email address and website | [email protected] https://www.ssembassydc.org/ |
| Diplomatic representation from the US | |
| Chief of mission | Ambassador Michael J. ADLER (since 24 August 2022) |
| Embassy | Kololo Road adjacent to the EU's compound, Juba |
| Mailing address | 4420 Juba Place, Washington DC 20521-4420 |
| Telephone | [211] 912-105-188 |
| Email address and website | [email protected] https://ss.usembassy.gov/ |
Key Political parties and their leaders in South Sudan
Info
International organization participation
All Important Facts about South Sudan
Want to know more about South Sudan? Check all different factbooks for South Sudan below.
-
 South Sudan Factbook
South Sudan Factbook
-
 The Economy of South Sudan
The Economy of South Sudan
-
 Learn about the Government of South Sudan
Learn about the Government of South Sudan
-
 Communication in South Sudan
Communication in South Sudan
-
 Popular Universities in South Sudan
Popular Universities in South Sudan
-
 Enerny in South Sudan
Enerny in South Sudan
-
 Transport in South Sudan
Transport in South Sudan
-
 The Geography and society of South Sudan
The Geography and society of South Sudan
-
 The Environment of South Sudan
The Environment of South Sudan
-
 Military and security in South Sudan
Military and security in South Sudan