Why Africa Has Two Congos: Unraveling the History and Differences
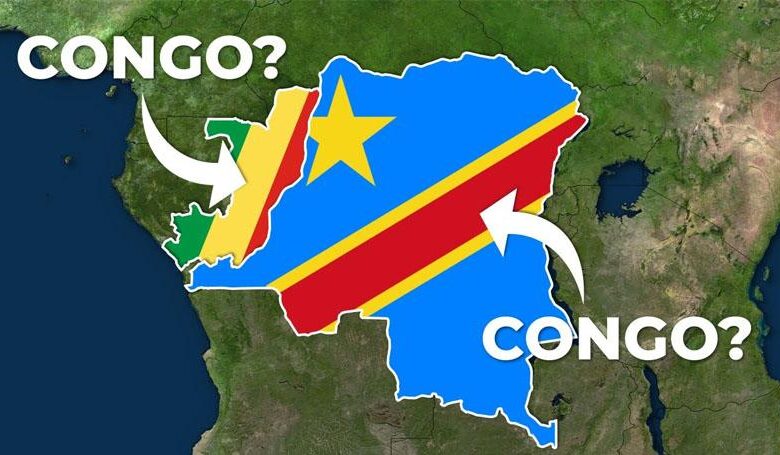
Africa is a continent rich in diversity, culture, and history. Within its borders, there are numerous countries, each with its own unique story. One intriguing aspect of Africa is the presence of two countries that share the name “Congo.” The Democratic Republic of the Congo and the Republic of the Congo are neighbouring nations that both derive their name from the Bakongo tribe and the Congo River. Despite this commonality, these two countries have distinct histories, geographies, and socio-political landscapes. In this article, we will delve into the fascinating reasons behind the existence of two Congos in Africa and explore the differences between them.
Exploring the Democratic Republic of the Congo
A Brief Overview
The Democratic Republic of the Congo, often referred to as Congo-Kinshasa, is the larger of the two Congos. Its capital city is Kinshasa, which is also the country’s largest city. Previously known as Zaire, the Democratic Republic of the Congo was a Belgian colony before gaining independence.
Geographical Features and Size
Situated in central Africa, the Democratic Republic of the Congo shares borders with several countries, including the Central African Republic, South Sudan, Uganda, Rwanda, Burundi, Zambia, Angola, and the Republic of the Congo. It boasts a vast territory, covering approximately 2,344,858 square kilometres, making it slightly larger than Mexico and about a quarter the size of the United States. The country has access to the Atlantic Ocean through a stretch of coastline at Muanda and the mouth of the Congo River.
Population and Culture
With an estimated population of around 95.89 million people as of 2021, the Democratic Republic of the Congo is one of the most populous countries in Africa. Its diverse population consists of numerous ethnic groups, each with its languages, traditions, and cultural practices. The country’s cultural heritage is rich and varied, encompassing music, art, dance, and cuisine.
Unveiling the Republic of the Congo
A Glimpse into History
The Republic of the Congo, also known as Congo-Brazzaville, is the smaller of the two Congos. Its capital city, Brazzaville, is situated on the western side of the Congo River. The region was initially claimed by the French in the 1880s and was named French Congo. It later became known as the Middle Congo.
Geographic Highlights
Covering an area of approximately 132,046 square miles, the Republic of the Congo is characterized by lush rainforests, diverse wildlife, and natural beauty. It shares borders with Gabon, Cameroon, the Central African Republic, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, and the Atlantic Ocean. The country’s flag, divided diagonally into green and red triangles with a yellow band, represents its agricultural and forest resources, as well as the noble character of its people.
Cultural Significance
The Republic of the Congo has a vibrant cultural scene, influenced by its French colonial past and indigenous traditions. Brazzaville, often referred to as the “Little Paris of Africa,” is known for its unique architecture, markets, and welcoming locals. The country is home to the Odzala-Kokoua National Park, a haven for wildlife enthusiasts and nature lovers, where Western lowland gorillas can be observed in their natural habitat.
Understanding the Differences
While the Democratic Republic of the Congo and the Republic of the Congo share a name and a border along the Congo River, they have distinct histories, cultures, and socio-political landscapes.
Historical Background
Both countries were shaped by European colonization, with the Democratic Republic of the Congo being a Belgian colony and the Republic of the Congo falling under French rule. The colonial era brought significant changes to the region, including the exploitation of natural resources and the introduction of Christianity.
Socio-Political Landscape
The Democratic Republic of the Congo has experienced considerable political instability and conflict throughout its history. Internal conflicts and external interventions have resulted in millions of deaths and widespread poverty. On the other hand, the Republic of the Congo has had a relatively more stable political environment, although it has also faced periods of unrest.
Natural Resources and Wildlife
Both Congos are blessed with abundant natural resources, including minerals, timber, and oil. The Democratic Republic of the Congo is particularly known for its vast reserves of copper, cobalt, and diamonds. The Republic of the Congo, with its dense rainforests, is home to diverse wildlife, including Western lowland gorillas, forest elephants, and buffalo.
Current Challenges and Future Prospects
Despite the challenges they face, both countries have shown resilience and are working towards stability and development. Efforts are being made to address issues such as poverty, corruption, and inadequate infrastructure. The potential for economic growth and tourism exists, with the Democratic Republic of the Congo’s Virunga National Park and the Republic of the Congo’s Odzala-Kokoua National Park attracting visitors from around the world.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the presence of two Congos in Africa is a result of historical events, colonial powers, and the unique geographical features of the Congo River. While they share the same name and border, the Democratic Republic of the Congo and the Republic of the Congo have distinct histories, cultures, and challenges. Understanding the differences between these two nations allows us to appreciate the complexity and diversity of Africa’s rich tapestry. As both countries strive for stability and development, there is hope for a brighter future for the people of the Congos and the continent as a whole